Transport Layer Protocols:
The main purpose of the Host-to Host layer is to shield the upper-layer application from the complexities of the network i.e this layer begin the processing of the gathered information ready to send.
Three protocols mainly work at this layer:
The main purpose of the Host-to Host layer is to shield the upper-layer application from the complexities of the network i.e this layer begin the processing of the gathered information ready to send.
Three protocols mainly work at this layer:
- Transmission Control Protocol (TCP)
- User Datagram Protocol (UDP)
- Stream Control Transmission Protocol (SCTP)
- TCP is a byte-oriented protocol: It receives a message or messages from a process layer, stores them as a stream of bytes, and sends them in segments.
- Sequenced: It number and sequences each segment so that the destination's TCP stack can put the segments back into the order the application intended.
- Connection-Oriented: Before a transmitting host starts to send segments down the model, the sender's TCP stack contacts the destination stack to establish a connection. The connection which is created is known as virtual-circuit.
- Reliable Service: Connection created between source and destination then data is transferred with acknowledgement and then connection is terminated.
- Acknowledgements: After data is send to the destination, acknowledgement is received whether data is reached or not.
- TCP is a full-duplex, connection-oriented. reliable, and accurate protocol.
- Flow Control: The receiver of the data controls the amount of data that are to be sent by the sender.
- Error Control: To provide reliable service, TCP implements an error control mechanism.
- Congestion control: The amount of data sent by a sender is not only controlled by the receiver(Flow control), but is also determined by the level of congestion in the network.
- Port no.= 6
- UDP is a message-oriented protocol: A process delivers a message to UDP, which is encapsulated in a user datagram and sent over the network.
- Unsequenced: UDP does not sequenced the segments and does not care in which order the segments arrive at the destination.
- Connectionless: UDP doesn't create a virtual-circuit between source and destination thats why it is connectionless.
- Unreliable Service: In this protocol, data is transferred directly i.e there is no surity whether data is reached or not to the destination.
- No Acknowledgements
- No Flow control, Congestion control
- UDP also provide error control(Checksum).
- Port no.= 17
- SCTP combines the best features of UDP and TCP.
- SCTP is a message-oriented protocol, it preserves the message boundaries and at the same time detects lost data, duplicate data, and out-of-order data.
- Full-Duplex Communication: SCTP offers full-duplex service, in which data can flow in both directions at the same time.
- Connection-Oriented Service: SCTP is a connection-oriented protocol.However, a connection is called an association.
- Reliable Service: It uses an acknowledgement mechanism to check the safe and sound arrival of data.
- Port no.= 2905
- Multihoming: A TCP connection involves one source and one destination IP address. This means that even if the sender or receiver is a multihomed, only one of IP address per end can be utilized during the connection whereas SCTP supports multihoming service i.e sending and receiving host can define multiple IP addresses.
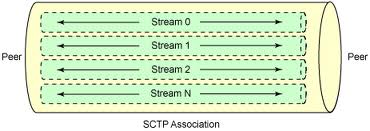
- Multiple Streams: An association in SCTP involve multiple streams.
- It also Provide Error control, Flow control, Congestion control.
Multihoming
Multiple Streams
Made By: P & V

No comments :
Post a Comment